In this article, we explain how to define key concepts for each lesson and then use key concepts to create quiz questions for each lesson.
Define Key Concepts for each lesson
Previously, we used Gardner’s theory of Multiple Intelligence to advocate for including a variety of learning activities to assist students who have different learning styles. Here we will look at a different theory of learning drawn from brain development research. It has become clear that there are different areas of the brain for short term and long term memory. One of our goals is to help students develop a long term memory of the most important concepts in our course.
One way of increasing long term memory is to cover the same key concepts in different contexts. Most people need to be exposed to key concepts at least three times in order for the brain to move the concepts from short term to long term memory. It is also important to limit the number of key concepts introduced with each lesson.
We have previously created a reading activity that includes about 5 to 10 pages of text and 5 to 10 images. We also included a 30 minute video that covers the same content and a 60 minute video conference that answers questions students may have about the same content. Thus, students are exposed to the content of each lesson 3 times.
However, it may not be clear to students what the key concepts of the lesson actually are. To make the key concepts of each lesson clearer, it is a good idea to summarize key concepts at the beginning of the reading assignment and include a review of key concepts at the end of the reading assignment.
The beginning summary can be statements and the ending review can be the same statements turned into questions. These questions can be followed by answers. Finally, the quiz on each lesson can include Key Concept Questions to further help students place key concepts for each lesson in their long term memory.
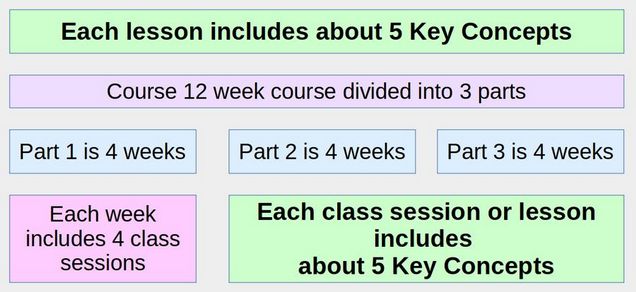
The number of key concepts may vary depending on the age of the student and the complexity of the course. For a grade school course, each lesson may have only one key concept. For a college level course, you might include up to 5 key concepts per lesson. Assuming there are four lessons per week, a college level course might introduce 20 key concepts each week. These 20 key questions are placed in a Moodle Question bank and then used to create the quiz associated with each lesson as well as monthly or quarterly quizzes which also help students move key concepts from short term to long term memory.
Use Blooms Taxonomy to Create Key Questions
A major problem with many online courses is the focus on low level knowledge. Low level knowledge is memory of simple facts. A person can remember a fact without understanding why a fact is important or what a fact is used for. Students who are limited to low level learning may be unable to apply the knowledge to a new situation or analyze when a concept should be applied. Worst of all, they may not be able to use the concept in combination with other concepts to create new work. These higher level abilities can be organized into a pyramid called Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Objectives.
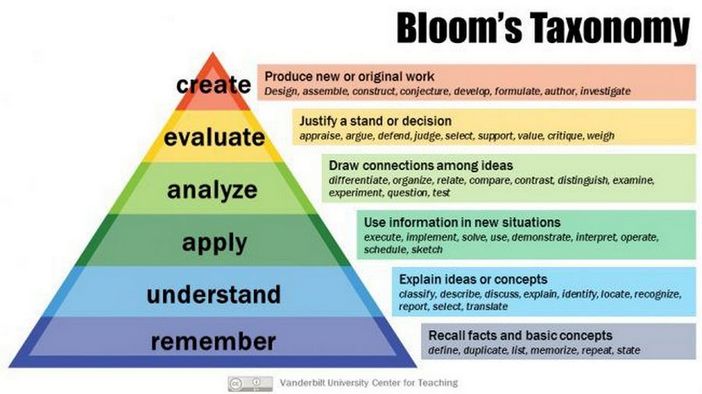
When creating quiz questions, it is important to create not only low level questions like defining a term, but also higher level questions like applying a concept to a new situation.
Learning Progression from simple to complex
Each level of Bloom’s taxonomy should be addressed before moving on to the next. Something can’t be understood without first remembering it; can’t be applied without understanding it; must be analyzed before evaluating it; and an evaluation needs to have been conducted before making an accurate conclusion. Students progress their way through Bloom’s Taxonomy levels sequentially with increasingly complex activities.
Level 1: Remembering Facts
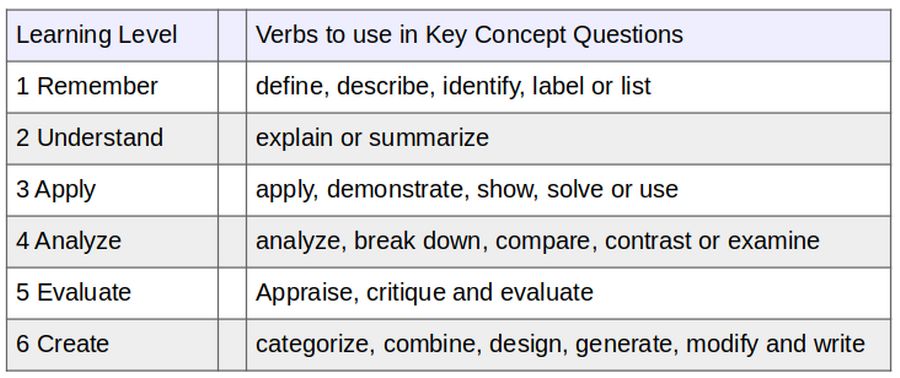
In the first stage of Bloom’s taxonomy, you might ask students to recite a key concept from reading material. Use verbs like define, describe, identify, label or list to turn key concept statements into key concept questions. Remembering key concepts is an important foundation; a stepping stone toward deeper learning. A basic way to test learning on this level is simple questions or multiple-choice questions. This shows that the student can memorize facts and recall them. But students may not fully understand the key concepts.
Level 2: Understanding Key Concepts
To evaluate student comprehension of key concepts, ask students to discuss a key concept in their own words and explain what the concept means and why it is important. To measure this, we can use verbs like explain or summarize.
Level 3: Applying Key Concepts
Projects are one way to help student take what they’ve learned and apply it outside of the classroom. Verbs to use in this stage include apply, demonstrate, show, solve or use.
Level 4: Analyze Key Concepts
Analysis includes asking students to use critical thinking skills to draw connections between ideas and break down key concepts into the its parts. This includes comparing and contrasting new key concepts from previous or similar information.
Key verbs for questions include analyze, break down, compare, contrast or examine. Critical thinking comes into play, as the student distinguishes between fact and opinion, and breaks information down into component parts.
Level 5: Evaluating Key Concepts
In the evaluate stage, the student justifies a decision by appraising a situation, arguing, defending, judging, critiquing or supporting their decision with thoughts based on the knowledge they’ve acquired. Appraise, critique and evaluate are good verbs to use.
Level 6: Use Key Concepts to Create New Work
In creating new work, the student applies what they learned to build something, either tangible or conceptual. That could include writing a report on a particular topic, designing a project, or revising a process to improve the results. Verbs to use include categorize, combine, design, generate, modify and write. Projects can range from essays that put parts of the learning together to form a whole concept or idea, or actual tangible projects like building a website.
Here is a table summarizing the above Learning Levels:
Below we will use these verbs to convert Key Concepts into Key Concept Questions.
Example of Creating Higher Level Questions
Let’s look at this process using the first lesson in our first course called Better Word Processing. The lesson title is 1.1 Word Processing versus Formatting. Lesson 1.1 is only 4 pages long and includes only 2 images.
Lesson 1.1 is deliberately shorter than other lessons in order to give students time to introduce themselves during the first class video conference. In addition, because the course is about Better Word Processing, it is important to help students understand what the term Word Processing actually means.
Step 1: Write the Lesson 1.1 reading assignment text
Step 2 Add images to the Lesson 1.1 reading assignment
Step 3: Review the Lesson Reading Assignment to pick out 5 key concepts
Sadly, the term word processing is often confused with the term formatting. The first page defines each term and points out the differences between the two terms. Thus, the first two key concepts are:
1.1-c1 Word processing is a broad topic that includes all tasks needed to create and share documents that are well organized and visually appealing.
1.1-c2 Formatting is a narrow term used to improve the appearance of pages, paragraphs, text, images, tables and lists.
The second page covers the difference between appearance and content and the difference between word processing tools and programs.
Thus, the remaining three concepts are:
1.1-c3 The term “content” includes text and images while the term “appearance” involves the way the content is displayed in an article.
1.1-c4 “Word processing tools” are functions that perform a specific task such as making text or font size bigger.
1.1-c5 “Word processing programs” are collections of word processing tools. Both Microsoft Word and Libre Office Writer are word processing programs that contain many similar word processing tools.
Step 4: Add the 5 key concepts to the beginning of the reading assignment.
Step 5: Convert the 5 key concepts into 5 Key Concept Questions
Below are our 5 key concepts turned into questions. While fill in the blank questions are more difficult to grade then simple True False questions and or Multiple Choice questions, they are needed to ask higher level questions.
1.1-c1 Word processing is a broad topic that includes all tasks needed to create and share documents that are well organized and visually appealing. (TRUE - FALSE)
1.1-c2 Explain how formatting is different from Word Processing.
1.1-c3 How is the term “content” different from the term “appearance” and why is this difference important?
1.1-c4 Describe at least two “Word processing tools”.
1.1-c5 How is the term “Word processing program” different from the term “word processing tools”? (Choose the correct answer)
A Word processing programs are more important than word processing tools.
B Word processing tools are more important than word processing programs.
C Word processing programs are made up of word processing tools.
D Word processing tools are made up of word processing programs.
E None of the above.
Step 6: Write short answers to the Key Concept Questions
1.1-c1 Word processing is a broad topic that includes all tasks needed to create and share documents that are well organized and visually appealing. TRUE!
1.1-c2 Formatting is a narrow term used to improve the appearance of pages, paragraphs, text, images, tables and lists. Word processing is a broader term that includes formatting and other skills.
1.1-c3 The term “content” includes text and images while the term “appearance” involves the way the content is displayed in an article. The difference is important because we may want to change the content without changing the appearance of our article – or we may want to change the appearance of our article without changing the content.
1.1-c4 “Word processing tools” are functions that perform a specific task such as making text or font size bigger, changing font colors, changing font families, changing image file size etc.
1.1-c5 “Word processing programs” are collections of word processing tools. (C)
Step 7: Add the Key Concept Questions and Answers to the end of the reading assignment
The reason to give students the answers to test questions in advance of the actual test is that the goal of assessment is not to fool students or rank students but rather to help all students achieve mastery of the 5 key concepts. Now that we have our Key Concept questions and answers we are ready to add them to our course question bank.
Question Bank and Quizzes
In order to assess student progress, you may want to create a quiz for each class session. Alternately, you can create a quiz for each weekly series combining Key Concepts Questions from four class sessions. Moodle has an activity called Quiz. However, the actual questions used in the quiz should be created and stored in a Course Question Bank before adding questions to any quiz. To add questions to the Question Bank, you need to assign yourself as the instructor for the course. Go to the course home page and click Participants. Then click Enroll users. Then type your name in the search box and assign the teacher role. Then click Enroll User.
Go to your Course Question Bank
To open the Question bank, first click on a course template or course you are the instructor for to go to the course home page. Then click on More in the Course Menu and click Question bank.
Sadly, the Question Bank category is still called Course Template. To change the Question Bank name to the name of your course click on Questions. Then use the drop down to select Categories:
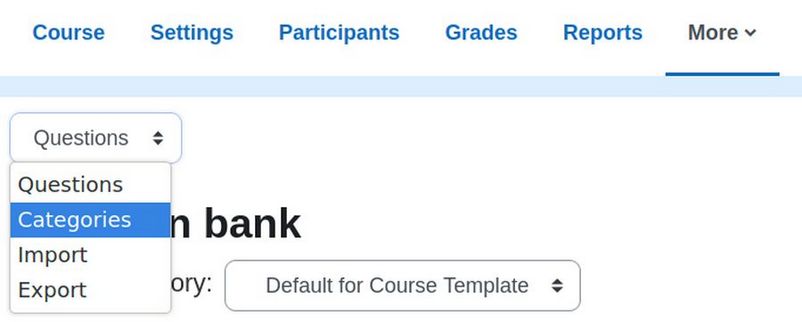
This takes us to this screen:
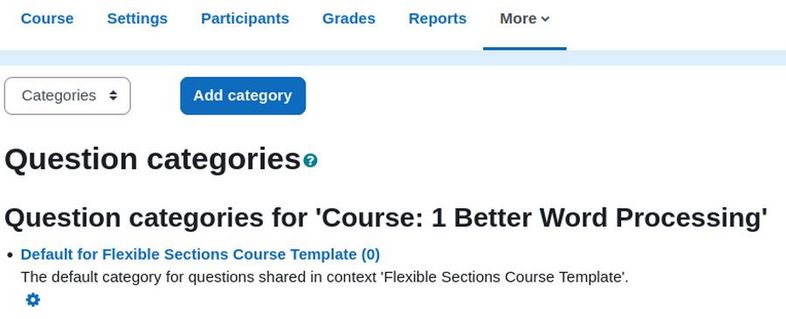
Click on the Settings wheel. Change the name to Default for Course 1 Better Word Processing. Change the Description to: The default category for questions shared in context '1 Better Word Processing'. Then click Save changes.
Before you create any new questions, you should first set up your Question categories. The Question Bank Categories screen includes question categories that have been created for this course and also for the Moodle Courses Category that this course was placed in and also a category called System which can include questions that can be shared across all courses. Below is our course template with no categories set up yet:
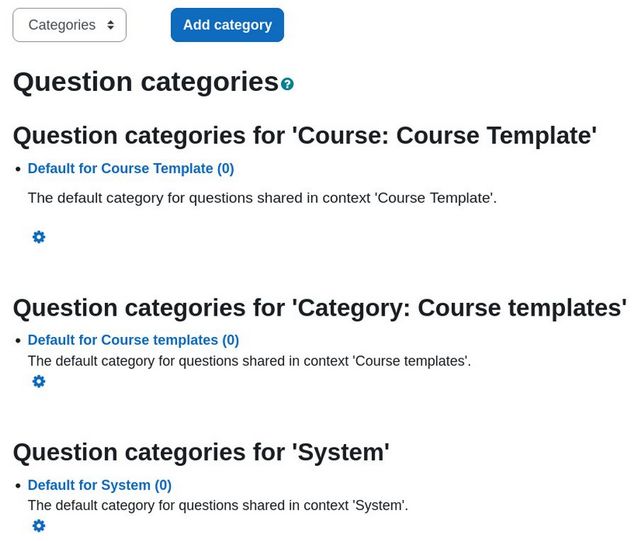
To add a new category, click Add category.
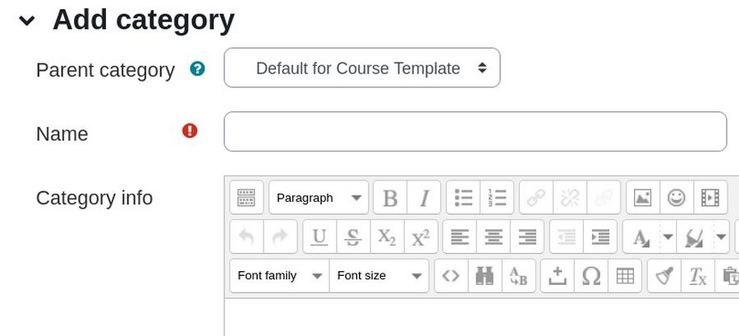
Because we have more than one quiz per week, we will first add Weekly categories and then later add each quiz as a sub category of our Weekly categories. Therefore name the first category, Week 1 Quizzes. Then click Save changes. Then click Add category and repeat until all 12 Weekly categories have been created. Here is what these weekly categories will look like:

We will next create a category for each quiz during Week 1. Click Add Category. Then for the parent category, choose Week 1 Quizzes. For name, type Quiz 1.1 Questions. Then click Add category and repeat to create a category called Quiz 1.2 Questions. Repeat to create categories for each of your four Week 1 quizzes.

Repeat adding categories to add four quizzes to the remaining 11 weeks.
Add Example Questions to Quiz 1.1
Use the drop down in the upper left to switch from the Categories screen to the Questions screen. Use select a category to choose the 1.1 Questions category. Then click Create a New question.
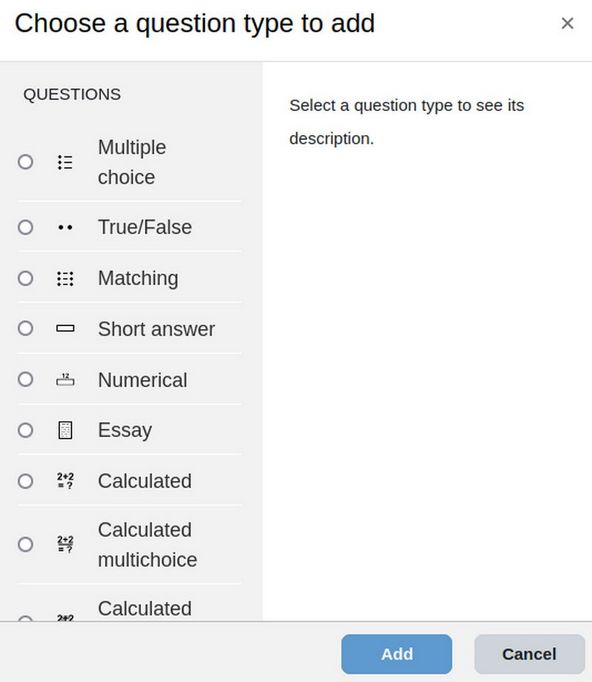
Scroll down the screen to see all 15 Question Types.
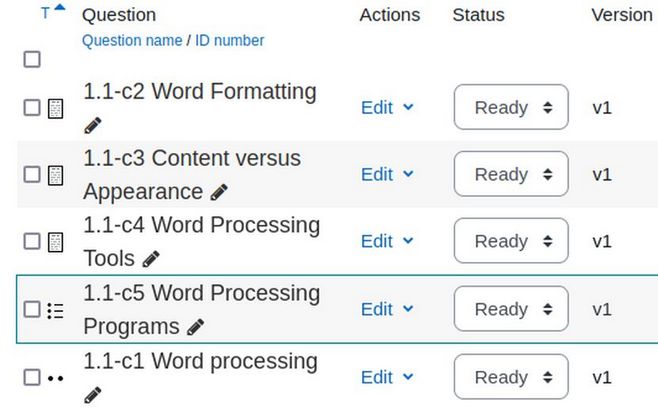
Here are our five questions we created for our Section 1.1 Key Concepts:
1.1-c1 Word processing
Word Processing is a broad topic that includes all tasks needed to create and share documents that are well organized and visually appealing. (TRUE - FALSE)
1.1-c2 Word Formatting
Explain how formatting is different from Word Processing.
1.1-c3 Content versus Appearance
How is the term “content” different from the term “appearance” and why is this difference important?
1.1-c4 Word Processing Tools
Describe at least two “Word processing tools”.
1.1-c5 Word Processing Programs
How is the term “Word processing program” different from the term “word processing tools”? (Choose the correct answer)
A Word processing programs are more important than word processing tools.
B Word processing tools are more important than word processing programs.
C Word processing programs are made up of word processing tools.
D Word processing tools are made up of word processing programs.
E None of the above.
The first question is a True False question. So click on the True False question type. Then click Add.
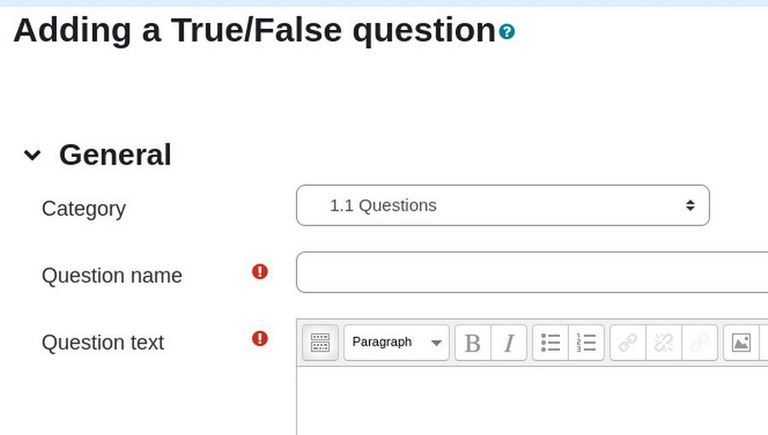
For Question name, type 1.1-c1 Word processing
For Question Text, copy paste: Word processing is a broad topic that includes all tasks needed to create and share documents that are well organized and visually appealing.
Select the text and change the font size to 14. Leave the default points at 1. Change the correct answer to True. Then click Save changes. Then click Create a new question to create the second question. This time, choose Essay. (note that the short answer question type only allows a few words). For Question name, type: 1.1-c2 Word Formatting
For Question text, copy paste: Explain in one or two sentences how formatting is different from Word Processing.
Change Response format from HTML to Plain Text.
Change input box from 10 lines to 5 lines. Copy paste one potential answer into the Information for Graders box:
1.1-c2 Formatting is a narrow term used to improve the appearance of pages, paragraphs, text, images, tables and lists. Word processing is a broader term that includes formatting and other skills.
Then click Save Changes. Repeat to add question 3 and 4 which are also essay questions. Here are the questions:
1.1-c3 Content versus Appearance
Explain in one or two sentences how is the term “content” different from the term “appearance” and why is this difference important?
1.1-c4 Word Processing Tools
Describe at least two “Word processing tools”.
Here are the Grader Information for these two questions:
1.1-c3 The term “content” includes text and images while the term “appearance” involves the way the content is displayed in an article. The difference is important because we may want to change the content without changing the appearance of our article – or we may want to change the appearance of our article without changing the content.
1.1-c4 “Word processing tools” are functions that perform a specific task such as making text or font size bigger, changing font colors, changing font families, changing image file size etc.
The final question is a Multiple Choice Question Type.
1.1-c5 Word Processing Programs
How is the term “Word processing program” different from the term “word processing tools”? (Choose the correct answer)
Note: Uncheck Shuffle the choices. Then copy paste in each of the five potential answers:
Choice 1: Word processing programs are more important than word processing tools.
Choice 2: Word processing tools are more important than word processing programs.
Choice 3: Word processing programs are made up of word processing tools. Grade 100%
Choice 4: Word processing tools are made up of word processing programs.
Choice 5: None of the above.
Then click Save changes. Here is the result:
Add Questions to Quiz Activity for Section 1.1
We have already created a quiz activity for Section 1.1 Turn on Edit Mode. Then click Course in the Course menu to go back to the Course Home page. Then in Section 1.1 Then click on the blue text for 1.1 Quiz to edit it. Then click Add Question.
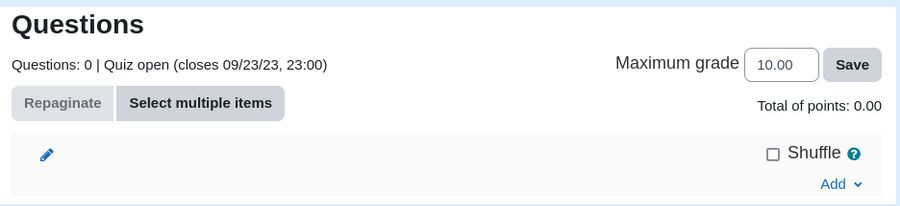
Click the Add button in the lower right corner.
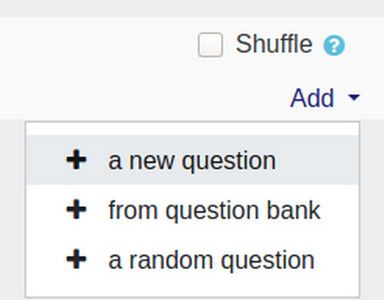
Then click Plus from Question Bank. Then select the 1.1 Questions category. Select the question(s) you want to add. We will select all five questions. Then click Add selected questions to the quiz.
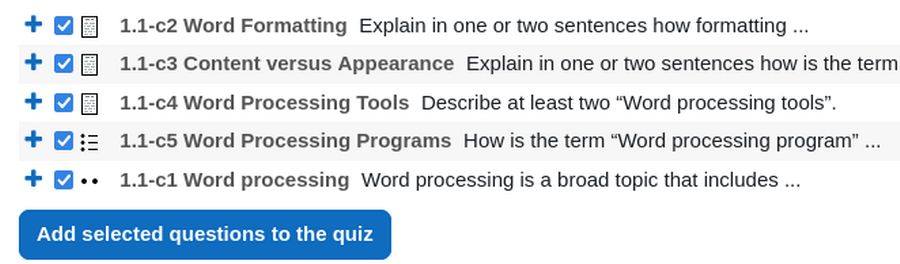
Change the Maximum Grade from 10 points to 5 points. Then turn off Edit mode. Click Quiz, Preview Quiz:
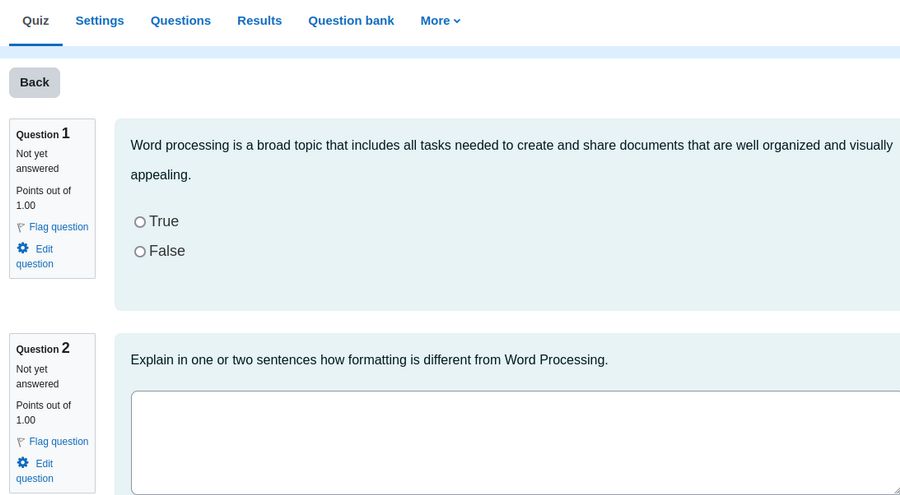
If needed, you can edit any of the quiz questions from here.
Add a student to the course to see if the quiz works properly
Click on the course in the breadcrumbs menu to go back to the course home page. Then click Participants. Then click Enroll User to add a Student Placeholder to the course. Then in a separate browser tab, log in as the student. Click on the blue text for 1.1 Quiz to take the quiz. Then click Attempt quiz. Then click Finish attempt. Then click Submit all and finish.
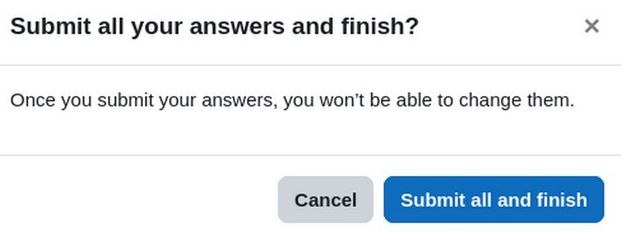
Click Submit all and finish. The correct answers are then shown. But it is shown as Not yet graded. Go back to the section and click Mark as done.
What’s Next?
In the next article, we will review how to grade the quizzes after they are submitted.

