In this article we will review the four primary roles in a Moodle online school program. These are the Tech Team, Administrators, Teachers and Students. The Tech Team manages the server, Administrators manage the school, Teachers manage the courses and Students participate in the courses.
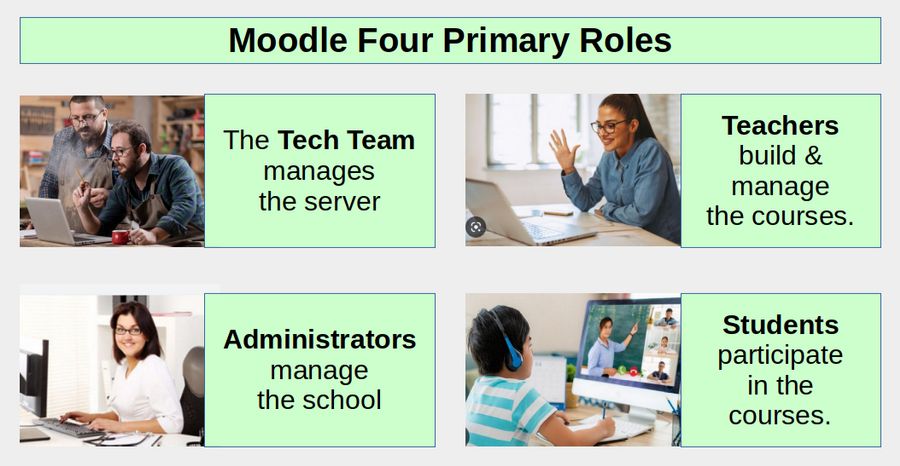
If you are setting up your own school to teach your own courses, you may be serving three of these four roles. But for training purposes, we will discuss the roles as if they were separate people – each with a clearly defined set of responsibilities. Let’s take a closer look at each of these four roles.
Tech Team Tasks
The Tech team uses a Linux computer to get a Hosting account. They use the hosting account to obtain a domain name and set up a Debian Virtual Private Server (VPS) connected to the domain name. They then use the host DNS Manager to create custom DNS records to point or connect their domain name to their VPS IP address. They then installed the Hestia Control Panel in the Debian VPS to to manage the VPS. They then use the Hestia Control Panel to create a User account with its own file system. In the Hestia User account, they insert the domain name and get an SSL.
They also set up a secure domain-related email system and create a database. They then use the Hestia File Manager to install Moodle. After installing Moodle, they set up a Cron job to update the Moodle database every few minutes and a Backup system to back up or take a copy of the website file system and database once a day. The Tech Team also sets up the Permissions for the website back end defining who can do what. Finally, they install a custom theme to configure the appearance of their Moodle website. We have covered these tasks during our first four chapters.
Over time, the Tech Team use the Hestia Control Panel to manage their server. This includes installing new Moodle Plugins, updating Moodle to the latest version, updating the plugins to the latest version and updating the VPS to the latest version of PHP. We will cover these ongoing tasks in our final chapter.

In addition, the Tech Team should assist teachers in setting up Joomla websites for each course where teachers can post the course curriculum and setting up video channels where teachers can post course videos.
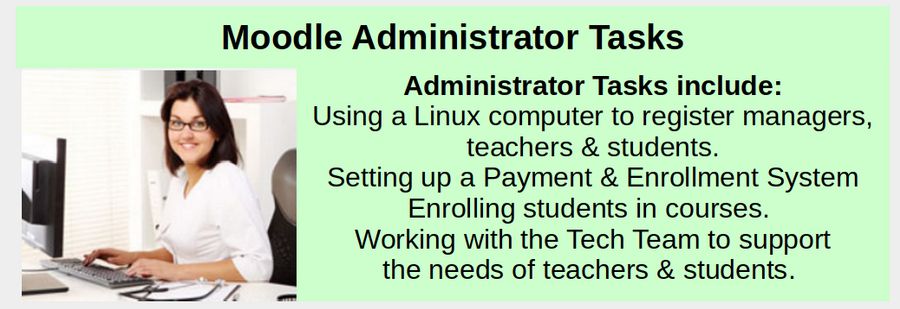
Administrator Tasks
Take a close look at most public and private schools and you will find a small group of administrators, a larger group of teachers and an even larger group of students. Administrators controls registration of managers (called Principals), teachers and students.
Administrators then use an online Payment System (called a Payment Gateway) connected to an Enrollment process to control the enrollment of students in courses. We will cover the Moodle Registration, Payment Gateway and Enrollment process in this chapter (Chapter 5).
Teacher Tasks
The Tech Team and Administration set up a Course Creation process so that all courses have a similar course format. In our case, we will use the Topic Course Format with a Flexible Sub section plugin. The Topic option allows us to create courses that are independent of time (compared to the weekly format which has a strictly defined time period). Teachers then develop the Course Curriculum and post it to a separate Joomla website. They also create Course videos and post them to a separate Course Video channel.

Teachers then use this Course Creation process to create each course including defining Course Content and Activities for each Class Session and setting up the Course Calendar.
We will cover the course creation process in more detail in Chapter 6. Teachers also build and run an evaluation system to help monitor student progress. We will cover this process in Chapter 7.
Importance of using Linux Computers
Note that for online security reasons, teachers, administrators and the Tech Team should use exclusively Linux computers when they are logged into the Moodle interface. Failing to use Linux computers risks allowing hackers to take over the back end of your Moodle website (and even taking over your Virtual Private Server) - compromising student data and destroying everything you have built! Note that taking daily backups does not address this problem because hackers often hide in your non-Linux computers and your server file system and database for months before taking action to lock up your computers and website and demanding a ransom payment.
It is essential to understand the importance of using Linux to build and run your Moodle online school. I once warned administrators at a large local college about the need to use Linux computers to run their online program. Sadly, the college administrators ignored my warning. A year later, their entire system was taken over and shut down by hackers who demanded a ransomware payment of over a million dollars. The college refused to pay the hackers and their entire school system was wiped out. More than one hundred instructors lost all of the online (and even offline) course they had spent years creating. The data of thousands of students was also compromised.
Students have fewer privileges on the Moodle website and therefore do not necessarily need to use a Linux computer to log into the student area of Moodle. However, every school that uses Moodle should also offer students a course on how to set up and use a Linux computer and encourage the use of Linux computers – as students using a non-Linux computer risk losing all of the work they have created in completing their course assignments. Hundreds of schools and thousands of businesses have been severely harmed by hackers – at a total cost of billions of dollars every year.
All of these hacking attacks can be prevented by converting the computers you use to Linux.
Student Tasks
Students use Moodle to structure their learning and keep track of their progress in the Course. This includes completing pre-class assignments (such as reading articles and watching videos). Active learning includes writing down questions noting anything they do not understand about the topics covered in the readings and videos. Students then participate in course activities such as attending video conference sessions – which are used to answer any questions the students may have about the assigned readings and videos.

Students then complete quizzes and build projects to help improve their skills. We will cover these tasks in Chapter 8.
How to allow guest access to your first course
One way to encourage potential students to sign up for your courses is to provide them with access to a free course. Allowing guest access to your first course helps students see how your online courses are structured as well as how much they can learn by taking your courses. There are three changes needed to allow guest access to a particular course.
First, log in with your administrator account. Click Site administration. Then click the Users tab. In Permissions, click User policies and check the box Auto-login guests. Then click Save changes.
Second, click the Plugins tab and scroll down to Authentication Click Manage authentication. Make sure the Guest login button is set to 'Show'.
Third, to allow Guest access to a particular course, go to the course you want to allow users to access as guests. From Course navigation, click 'Participants', and then from the Enrolled Users dropdown, click Enrollment methods:
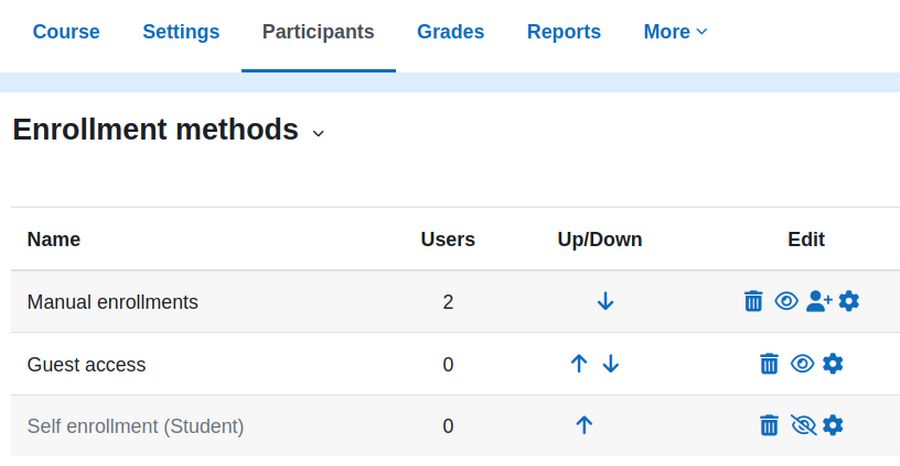
Enable guest access by clicking on the "eye" icon or by choosing it in the 'Add method' dropdown menu. Then without logging in, go to Courses and click on your first course to make sure you can view it as a guest.
What’s Next?
In our next article, we will take a closer look at the Moodle process for registering administrators, managers, teachers and students.

