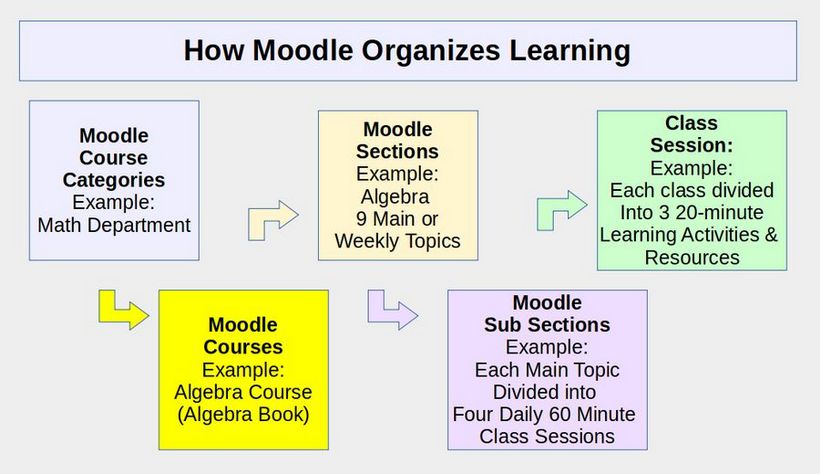
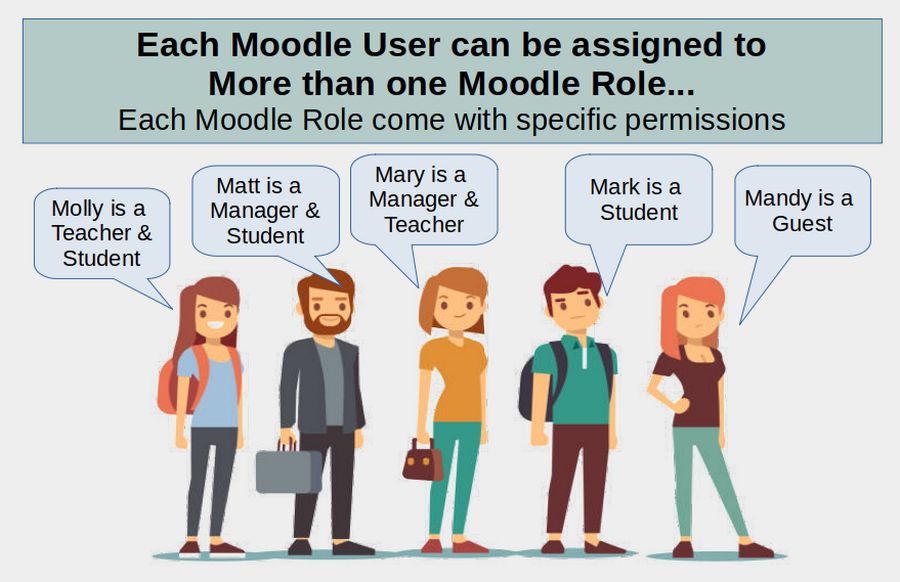
In this article, we will set up our own system of Placeholder Users in part as a learning exercise but also to demonstrate a flexible User system that can be adjusted for any Moodle website. As we noted in our previous article, each Moodle User can be assigned to several different roles
Default Moodle Roles and Permitted Actions
Moodle provides five primary roles each of which is given a specific set of possible actions. Here is a table of Moodle roles and actions:
|
Actions
|
Admin
Manager
|
Teacher
|
Non-edit
Teacher
|
Student
|
Guest
|
|
View
Courses
|
yes
|
yes
|
yes
|
yes
|
yes
|
|
Participate
in Course Activities
|
yes
|
yes
|
yes
|
yes
|
x
|
|
View student records
|
yes
|
yes
|
yes
|
x
|
x
|
|
Add and edit course activities
|
yes
|
yes
|
x
|
x
|
x
|
|
Create New Courses
|
yes
|
x
|
x
|
x
|
x
|
|
Set Roles &
Permissions
|
yes
|
x
|
x
|
x
|
x
|
Customize our List of User Roles
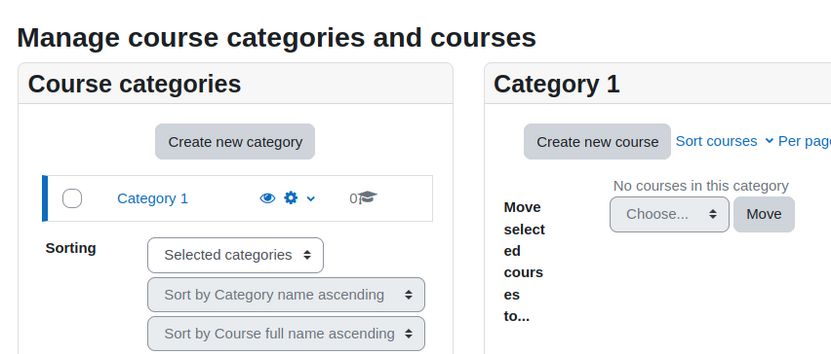
Before we create our own list of users, we need to create the list of custom roles we want to assign them to. Log into your default Moodle site (or the Moodle Sandbox site). Then click Site administration, Users, Permissions, Define roles. There are 8 default assigned roles:
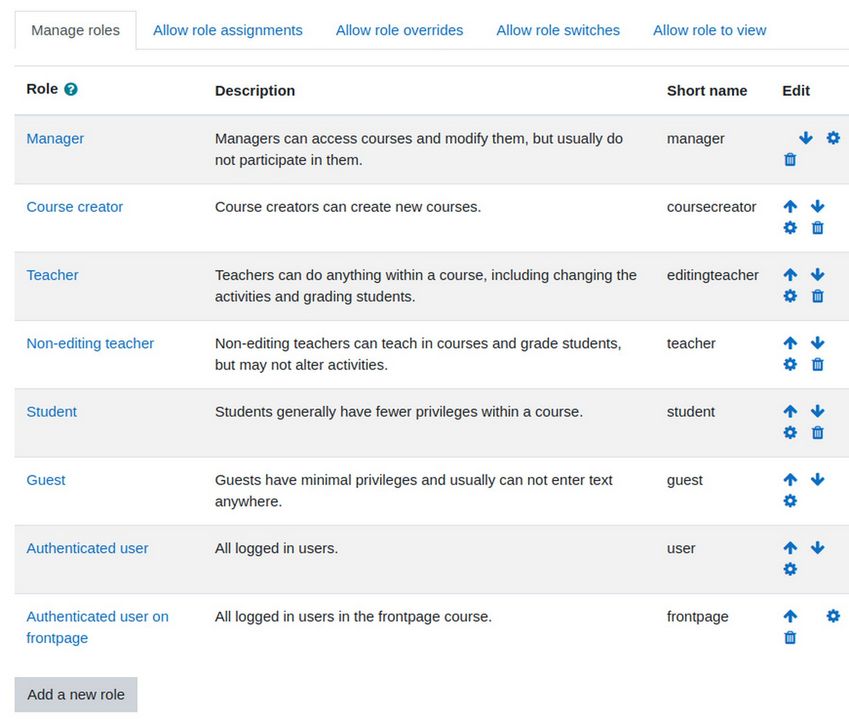
Note that this does not include the Administrator role, which Moodle defines in a separate screen. The difference between a Moodle Administrator and a Moodle Manager is that a Moodle Administrator has all permissions - and these permissions can not be edited or changed. There must always be at least one Moodle Administrator (the person who created the Moodle website).
A Moodle Manager also has nearly all permissions. However, the permissions given to a Moodle Manager can be changed by a Moodle Administrator and can be flexible to whatever the role of Manager is in a given Moodle Organization structure.
Three steps to take before creating new custom roles
Each new custom role will add more than 350 new permissions elements to your database. I therefore recommend only adding 3 to 5 new roles at a time. Before we start, go to the Dashboard page and make sure that Customize this page is turned off. Also go to the Home page and make sure that editing is not turned on. Finally, click Admin, Developer, Clear Cache prior to creating new roles.